Other Interacting-for-Benefit Approaches
THEE's Framework
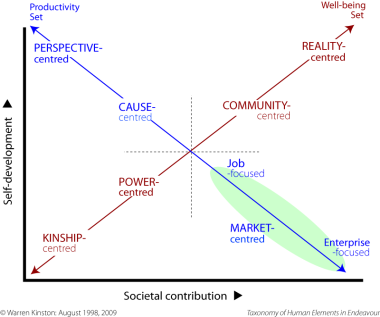
THEE identifies seven discrete and incompatible approaches to as shown.
| ● | ~R&T's Individualist |
| ● | |
| ● | |
| ● | |
| ● | ~R&T's Expert |
| ● | ~R&T's Opportunist |
| ● |
Opposing Demands on Leaders
Again, note that two very different sets of approaches are found on the two diagonals. The two opposite groups of method are about:
● ensuring our well being
.
Life in general is tough, but being productive can be especially difficult. To cope with this, we all need to have a way to feel good. Leaders must bear disappointments and take responsibility for failures. So maintaining their own morale is important, sometimes the top priority.
Pairing Ways of Interacting-for-Benefit
Pairing them reveals the usual preference for either the same degree of being productive (vertical lines) or of feeling good (horizontal lines). Some typical combinations are shown. See a fuller account here.
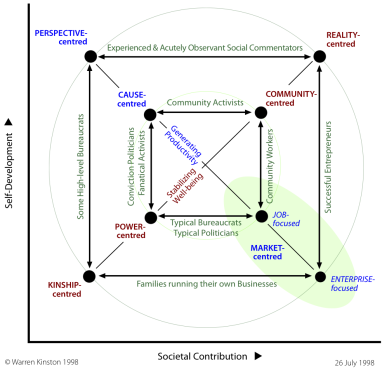
Leaders need to be attentive to the well-being (morale) of their group and to their productivity. Two categories of leader were identified by R&T:
■ the : R&T's Expert;
■ the : R&T's Opportunist.
Both are in the left half of the TET i.e. low on making a contribution — but at least not extremely low. Given that R&T probably dealt with businesses, it is noteworthy that none of their leaders were described as or . That surely tells you something.
- Were any leadership categories related to these methods missed by R&T?
See the answer (and its picture).
Last Updated: 12-Jan-2012